OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing Features
Set security attributes on sensitive resources
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Zero Trust Packet Routing uses security attributes (essentially metadata) to identify and organize resources. With it, you can assign security attributes to OCI resources, such as databases and compute instances. You can then create OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing policies that reference those security attributes. These policies are enforced at the network layer to block traffic through any unauthorized paths.
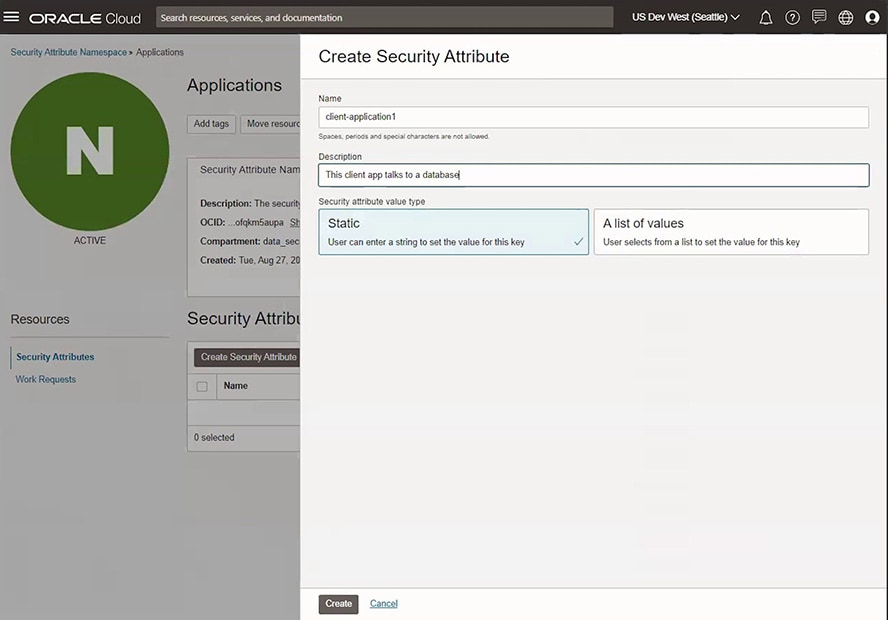
Write network security policies in natural language
OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing’s policy language makes it simple to create rules that specify which resources are allowed to communicate. These policies reference metadata about the specific data resources being accessed and their associated security attributes. Access is permitted only from a specific originator (such as a compute instance) to a designated data resource. If an authorized request attempts to access the resource outside of the defined path, it will be denied.
Although unprotected databases with guessable credentials can be breached within minutes, just one line of OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing policy can help prevent databases from being exposed.
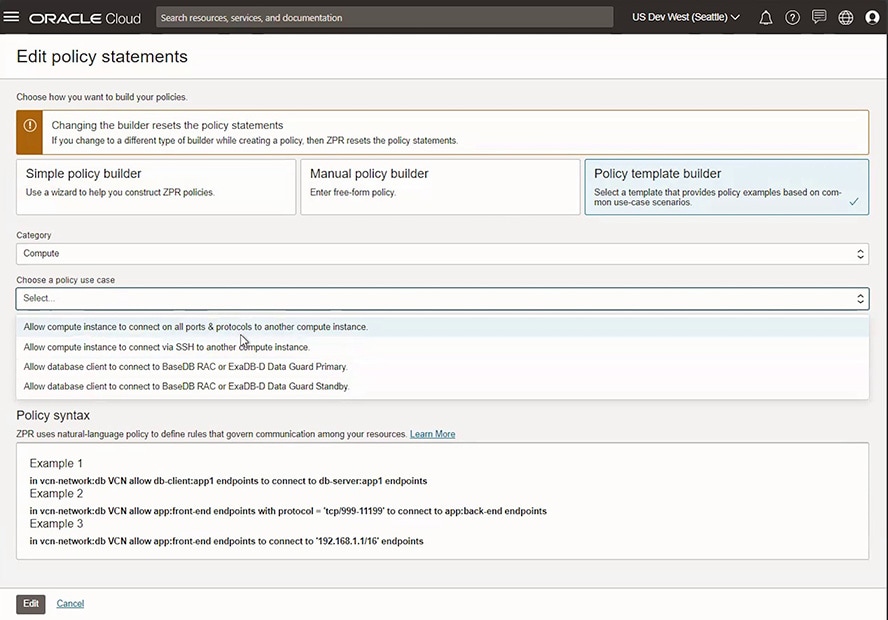
Separate network security from network architecture
Using a traditional network architecture–based security approach is time-consuming due to the complexity of securing and auditing multiple network configuration points. Additionly, the responsibility for implementing security policies often falls to network teams, whose typical goals of low latency and high availability don’t always align with security goals. OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing helps address these challenges by separating network security from network architecture, letting security teams create policies that are enforced at the network layer. OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing dramatically helps reduce complexity by letting network administrators run a flat network while security teams protect resources as intended.
Streamline compliance
OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing helps simplify audit and compliance processes by establishing clear intent-based policies and applying security attributes to resources. Without it, understanding access required auditors to manually review subnets; CIDR blocks; routing tables; security groups; network access control lists; and detailed rules based on IP, port, protocol, and firewall configurations defining ingress and egress restrictions. OCI Zero Trust Packet Routing helps reduce the effort needed to analyze and understand which hosts and services can communicate with each other.
Auditors can rest assured that security policies apply to all appropriately labeled resources, even as network configurations change.